Wiper seals are also known as Scraper seals. They tend to be used in conjunction with other sealing elements. Wiper seals create a tight fit whilst still allowing a reciprocating ram rod to pass through the inner bore of the seal. Despite its important function, the wiper seal is possibly the most undervalued seal type in the hydraulic cylinder. Wiper seals are used to eliminate contaminants such as moisture, dirt, and dust. Contamination can cause significant damage to the rod, cylinder wall, seals, and other components. This is one of the primary causes of premature seal and component failure in a fluid power system. Some Wipers or Scrapers have a secondary lip used to capture any oil that may have bypassed the main seal. The secondary lip may also remove any bonded contaminate from the rod surface.
Rod seals are considered the most critical element of a cylinder sealing system. They prevent the leakage of fluid from within a hydraulic cylinder to the outside as the rod cycles back and forth (dynamic pressure sealing). Rod seals work together with wiper seals to protect a hydraulic system against external contaminants such as dirt and outside weather conditions. Rod seals are static seals installed in the glands or housings. They maintain a seal with the piston rod in dynamic motion. In heavier duty applications, a rod seal can be combined with a secondary buffer seal for a more robust sealing effect.
Piston seals or piston rings ensure fluid or other media does not by-pass the piston as the system pressure pushes the piston down the cylinder during a pressure cycle. Piston seals are dynamic seals, typically single-acting (pressure acting on one side only) and double-acting (pressure acting on both sides) seals. The choice of piston seal is determined by the way in which the cylinder operates. Single-acting pistons only contain pressure on one side of the piston. The seal is required to retain pressure from that direction, which then moves the piston along the cylinder. Double-acting pistons contain pressure on both sides of a piston without leakage. They allow maximum mechanical effort to the moving the piston along the bore of a cylinder. For a cylinder which is exclusively single-acting, capable of sealing dynamic pressure from one side (unidirectional), it is always best to choose the type of seal designed to provide optimum sealing qualities for single-acting functions. The best sealing capacity of a double-acting cylinder, capable of sealing dynamic pressure from both sides (bidirectional), is achieved by choosing a double-acting seal. A piston design where two single-acting seals on the piston for a double-acting cylinder are used can easily give rise to a breakdown. The reason is that a very high pressure can be trapped between the seals. Piston seals, both single and double-acting, can be designed for and used with integrated or separate back-up rings and guide rings.
Mining seals usually are multi-part seals with additional back-up rings and preloading elements in order to meet the increased requirements. Pertaining to their geometry these seal types resemble the usual piston- and rod seals, but they got adapted to the comparatively high hydraulic pressure of mining applications.
Wear rings are used to help keep the piston cantered, which allows for even wear and pressure distribution on the seals. These seals are used in both piston and rod applications. Wear rings should be installed on the lubrication (wet) side of the seal for best performance. For rod glands, the wear ring should be on the pressure side of the rod seal. For pistons, if only one bearing is to be used, it should be on the side of the piston opposite the rod. This arrangement keeps the piston wear ring further away from the rod wear ring. This becomes critical when the rod is at full extension and provides better leveraging of the two bearing surfaces. Popular materials include glass filled Nylon, bronze filled PTFE and glass filled PTFE. Wear rings are available in butt cut, angle cut and step cut styles. Straight cut, also known as Butt Cut rings are the easiest style to install in many applications. Straight cut rings are best suited for rotary movement. Angle cut rings improve bearing stress at the gap. These rings tend to suit reciprocating movement.
Back-up rings, or anti-extrusion rings, are thin rings that are designed to prevent O-ring extrusion under pressure. They fit in the gland between the seal and the clearance gaps to provide zero clearance. Read on to find out more about the function of these invaluable parts. Back-up rings provide added resistance support to a seal and minimise the risk of extruding a seal in its housing when under pressure. Back-up rings, sometimes known as anti-extrusion rings, are not designed to have any sealing function in their own right. They are simply there to support the actual sealing elements of a design and stop them extruding under higher pressures, or where metalwork clearances are larger than is ideal. Back-up rings for O Rings can be contoured or flat, depending on the design requirements of the sealing system. They can come in the form of a solid ring, a split ring or even a spiral ring, depending on the environment that the back-up ring is expected to operate in, and for ease of fitting. Extrusion under pressure can happen to almost any type of seal, not just O Rings. Back-up rings are placed behind the seal if it is a single acting system, or both sides if double acting. Back-up rings are always made of a harder material than the seal itself to minimise the amount of extrusion in the sealing gap of the seal housing. They do this by supporting the sealing element itself with a close fit to the housing. When greater sealing and system forces are anticipated, the more precise the fit of the parts must be. Consideration must always be given to the environment expected for any particular seal and its back-up rings. It is also important to consider the degree of acceptable friction losses, in order to provide the most suitable solution, as a back-up ring may increase the friction present within a system.
Static seals are used in hydraulic applications where two mating surfaces or edges require positive sealing. A static seal, by definition, is one that remains stationary and subjected to no movement and its related friction. A static seal may be exposed to hydraulic pressure on both sides or be exposed to hydraulic pressure on one end and air on the other. Most often in hydraulics, static seals are used to seal a body, flange or head to another stationary tube, cap or other components. In a hydraulic cylinder, static seals are used to seal the barrel to the head and cap in tie-rod cylinders, or perhaps the head or gland of a welded cylinder. Once again, these static seals must prevent internal pressure from escaping. Static seals used to seal a tube in tie-rod cylinders are especially prone to failure if extrusion gaps are too large, allowing tie-rod stretch to loosen gaps and provide a path for extrusion. Static seals are often just an O-Ring, but when extreme pressure is possible, harder rubber or plastic backup rings will sit behind the O-Ring to support it as it’s exposed to pressure. In places where extrusion gaps are minimal, such as pump housing, backup rings are rare.
The Rotary Shaft Seal is used for excluding dirt, dust, water or other particles, while retaining lubricant in rotary shaft equipment. It was developed as a means of protecting bearings of rotating shafts. The sealing effect is achieved by preloading the sealing lip making its internal diameter slightly smaller than the shaft diameter. The garter spring ensures constant force to the shaft, flattening the sealing edge to a defined width. Rotary shaft seals are used between rotating and non-rotating machine components. They are comprised of:
Guiding tapes serve as bearings between the metallic components of the unit during piston stroke and in static conditions. They prevent metallic contact between pistons and cylinders or rods and glands where forces act perpendicular to the direction of movement. The guiding tape is continuous, wound as a flat coil or spiral preform, and can be cut to any desired length.
Key properties

V-rings seal axially against a counter-face. This type of seal has proved to be reliable and effective against dust, dirt, water and oil splash and other media. V-ring shaft seals provide effective protection against dry and wet contamination. The V-ring also reduces wear and extends the service life of the oil seal and bearings. The V-ring also performs well in dry running applications. Because it is all rubber and very elastic, it can be stretched over flanges or other components for easy installation with very little dis-assembly.

In Aftermarket world, the custom-made sealing kits are some of the main components in various parts. Among those who purchase these types of parts are industrial vehicle, hydraulic equipment and pneumatic equipment manufacturers. In Aftermarket, the scale of requirements has led these large companies that use the seals, across all fields, to source them from a large number of suppliers, thus multiplying the number of seals sold and included in a kit.

O-rings are unique in this list since they are identified primarily by their shape rather than by their location or specific function. As their name suggests, O-rings are donut-shaped and come in many different materials (e.g. rubber, silicone, fluorocarbon) and sizes (e.g. less than an inch to several meters wide). When these types of seals are mechanically deformed by pressure, they create very effective sealing barriers. Due to their low cost and relative simplicity, O-rings are the most common type of hydraulic seal on the market today.
X rings (also known as quad or square rings) are, in essence, enhanced versions of O-rings. Their four-lobed design allows them to achieve up to twice the sealing power of normal O-rings with less mechanical deformation. X rings can be used both as static seals and as dynamic seals.

Rubber Cord is an O-Ring Profile available in running lengths and in various cord diameters. The rubber cord can be profile cut to required angle and both ends joints with the help of an adhesive to form a circular ring. Rubber Cords form a very useful substitute to sudden break down Jobs and helps in saving time to get expensive assemblies executed, instead of waiting for an endless O-Ring ordered or to be procured. We offer a large selection of rubber cord in metric and inch cross sections by metre to any length. Rubber Cords are supplied in Standard Sealing material NBR, FKM, Silicone (VMQ), Neoprene (CR), Ethylene-propylene (EPM/EPDM)

We have variety of O-Ring kits of UK and US standard sizes, our O-Ring Kit is industry standard. O-Ring kit contains 30 sizes of o-rings in total quantity 382 pieces of o-rings of the most often used AS568 Standard sizes. The outside top cover has detailed, labels indicating the sizes and quantities of the o-rings in each compartment.

Oil seals – often called grease, fluid or dirt seals – close spaces between stationary and moving components in mechanical equipment, helping prevent lubricant escape. They also stop harmful contaminants from entering machinery, particularly in severe environments. Vital components of practically every type of machine and vehicle in operation, oil seals protect all types of precision-constructed, close-fitting ball, sleeve and roller bearings. In precision bearings, oil seals help prevents lubricants from escaping the bearings or a specific area. In machine components, oil seals help prevents abrasives, corrosive moisture and other harmful contaminants from entering machinery. They also help stop intermixture of two different mediums, such as lubricating oil and water.

A diaphragm seal is a flexible membrane that seals and isolates an enclosure. The flexible nature of this seal allows pressure effects to cross the barrier but not the material being contained. Common uses for diaphragm seals are to protect pressure sensors from the fluid whose pressure is being measured. Since diaphragm seals need to be highly flexible, elastomers are commonly used, and include a wide variety of both general purpose and speciality rubbers. Elastomers are limited to low pressure applications and those that are chemically compatible with the various plastics and rubbers used. Depending on the PSI levels of the sealing application, the diaphragm may require fabric reinforcement. Diaphragm seals (also known as chemical seals or gauge guards) are also used to protect a process fluid from the pressure sensor. Examples of this use are:

Bonded Seals are also known as Dowty Seals or Dowty Bonded Washers. They are high pressure seals which are used in the Mechanical, Hydraulic and Pneumatic sectors. Bonded Seals were originally designed to replace copper-type washers that are used in high-pressure systems. They comprise of a metal washer and an elastomeric ring which is bonded inside the diameter. The metal washer prevents over-compression and limits deformation of the elastomeric ring. Rubber to metal bonding is an ideal process for manufacturing components and parts including; valve assemblies, shafts and rollers. Additional uses for this process include rubber components bonded to steel, aluminium and brass. These parts are commonly used in the Rail and Transport industries. Rubber to metal bonded parts can be produced in a wide array of sizes and shapes. Rubber to metal bonding is a method where rubber is mechanically bonded to metal during the rubber moulding process. By combining components into one part rather than have two or three separate components not only results in potential cost savings, but also provides a more consistent and technically superior solution. The process used to bond rubber to metal depends on the application, specifically how the finished part will be used. To achieve a successful bond, much of the value lies in mould tooling design, surface preparation processes, primer selection and curing configuration (temperature, pressure and duration).

Gaskets are mechanical seals which fill the space between two or more mating surfaces. They are generally used to prevent leakage from, or into the joined objects while under compression. A gasket allows “less than perfect” mating surfaces on machine parts where they can fill irregularities. Gaskets are commonly produced by press cutting from sheet materials. However, should your application require a non standard or bespoke thickness; we can offer fully moulded gaskets at competitive prices. Traditionally Asbestos was a common gasket material for applications such as high pressure steam systems. Due to the health hazards associated with it, compressed non asbestos fibres (CNAF) are now used in its place. Ideally a gasket should be made from a material that is to some degree yielding, such that it is able to deform and tightly fill the space it is designed for. This includes any slight irregularities. Some joints may also require an application of sealant directly to the gasket surface to function properly.

Extruded rubber seals support complex cross-sections and a smooth surface finish. Extrusions from EPDM, FDA approved materials, silicone extrusion seals, neoprene extrusion seals, nitrile extrusions, FKM extrusion seals, bulb seals, accordian extrusion seals, PVC sponge extrusion seals, sponge rubber extrusion seals and many other compounds. Seal extrusions are used for many applications including door seals, vacuum applications, nuclear door seals, marine door seal, oven door seals, and many more applications in medical, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries. Extrusion seals can be manufactured with pressure sensitive adhesive backing, and can be made as inflatable (pneumatic) extrusion seal for a tighter seal. Extrusion can be done in different shapes ie. Square, rectangle etc, and in intricate shaped profiles as per your drawings or samples. We can customize your rubber products in different colours and polymers. Below are polymers you can select from.

PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is an inert material which makes it resistant to nearly all chemicals and acids. It is also self-lubricating, making it great for applications which are either dry, or have an abrasive media. PTFE products are manufactured from the blending of virgin PTFE with various fillers. There are hundreds of different PTFE materials with a variety of fillers. Common fillers include glass fibre, carbon, graphite, molybdenum disulphide, metal oxides and various polymers. Each possesses different properties, appropriate for different applications and service conditions. Common to all filled PTFE materials are their improved resistance to wear and deformation. PTFE finds diverse applications in various industries such as chemical , pharmaceutical, electrical, power plants , fertilisers, paper, railways, shipping, aircrafts, spacecrafts, machine tools manufacturing etc, practically all kinds of industries are demanding PTFE for existing and new applications due to its unique and exceptional properties.
Our PTFE product range includes; PTFE Moulded sheets, Expanded PTFE, Modified PTFE, PTFE Moulded Rods, PTFE Bushes and tubes, PTFE Bellows, PTFE Disc and Circles, PTFE Skived sheets, PTFE Dimple sheet, PTFE Bridge bearing pad, Peek PTFE, PTFE Ball valve set, PTFE Thrust washer gland packing, PTFE Extruded rod, PTFE rings and washers, PTFE Gaskets, PTFE Envelops, PTFE O/V/C/U/D rings, PTFE Strips, PTFE Float, PTFE Cup type packing, Pigmented PTFE, PTFE Balls, PTFE Diaphragms, PTFE Nozzles, PTFE Liner, Filled PTFE products and other customised products.

Cast Nylon is an extremely versatile thermoplastic resin. It can contribute significantly to weight and noise reduction, lubrication savings, and gear life extension and as an engineering material, cast nylon is highly resistant to impact, wear, and vibration. Its physical properties and price point make it a superior choice over metal and rubber in many mechanical applications. Cast nylon has almost limitless production possibilities. It is easy to machine and fabricate since part size and thickness are almost unlimited without degradation of the material. Additives such as glass, oil, or Kevlar fibre can be mixed in during processing to strengthen the final product. Cast nylon is available in a wide variety of colours, including black, blue, dark gray, green, and natural. Cast nylon also meets FDA standards. Cast Nylon offers one of the largest range of sizes and custom shapes of any thermoplastic. Nylon Castings are available in rods, tubes and sheets. Cast Nylon has significantly greater heat deflection temperature, better solvent resistance, better hydroscopic characteristics, and better dimensional stability than extruded Nylon. In addition, a large variety of dry, solid, and oil base fillers can be added to make products better suited for more challenging applications.
Our Nylon product range includes; Gear, Bushes, Pulleys, Sprockets, Pads, Blades, Rollers, Rods, Sheets, Plates, Pipes, Tubes, Rings , Strips, Liners, Discs, Sleeves, Wheels, Guide ways, Couplings and other customised products.

Polyurethane is an extremely versatile elastomer used in countless applications worldwide. Polyurethane's mechanical properties can be isolated and manipulated through creative chemistry which creates a number of unique opportunities to solve problems with performance characteristics unequalled in any other material. Polyurethanes are outstandingly able to withstand more loads than rubber because they are harder than rubber and yet more flexible than plastics. Their flexibility is accountable for their strength and remarkable ability to resist impact. Polyurethane has a high load capacity in both tension and compression. Polyurethane may undergo a change in shape under a heavy load, but will return to its original shape once the load is removed with little compression set in the material when designed properly for a given application. Polyurethanes perform very well when used in high flex fatigue applications. Flexural properties can be isolated allowing for very good elongation and recovery properties. For applications where severe wear prove challenging, polyurethanes are an ideal solution even at low temperatures. Polyurethane bonds to a wide range of materials during the manufacturing process. These materials include other plastics, metals and wood. This property makes polyurethane an ideal material for wheels, rollers and inserts. Polyurethane is very resistant to extreme temperature, meaning harsh environmental conditions and many chemicals rarely cause material degradation.
Our PU product range includes; Diaphragms, Bushes, Pulleys, Sprockets, Pads, Rollers, Rods, Sheets, Plates, Pipes, Tubes, Rings , Strips, Liners, Washers, Spiders, Discs, Sleeves, Wheels, Guide ways, Couplings and other customised products..

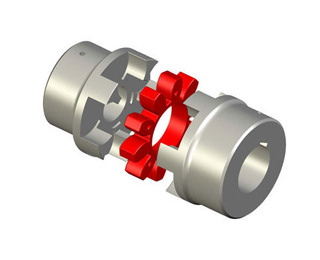
First and foremost, jaw couplings are popular because they are versatile and robust. They operate in a wide band of temperatures, can handle angular misalignment, can handle reactionary loads due to misalignment, have good torque to outside diameter capability, have good speed capability, good chemical resistance (spider dependent), and decent dampening capability.They are easy and straight forward to install. A basic jaw coupling is comprised of only 3 main parts, two hubs, and an elastomeric spider or insert. The elastomer of the spider can be made in different materials and hardness, which allows the user to customize the coupling to best serve their application. Considerations for elastomer selection include ability to dampen vibration, ability to handle misalignment, operational temperature range, speed of equipment, and chemical conditions. Jaw couplings are considered "fail-safe" because, should the elastomer fail or wear away, the jaw coupling hub teeth will mate, much like teeth on two gears, and continue to transmit torque. This may or may not be desirable to the user depending on the application. Jaw couplings elastomers are wearing elements that do need to be inspected and replaced. Jaw coupling elastomers often have signature wear patterns, and failures can often be root caused based on the condition of the elastomer and hubs. Common failure causes include misalignment, over-torque, chemical exposure, temperature exposure, torsional vibrations, and hub failure.